

 Vol. 39 (Nº27) Year 2018. Page 21
Vol. 39 (Nº27) Year 2018. Page 21
Alexey Alimovich SHAKHMAMETYEV 1; Irina Aleksandrovna STRELETS 2; Kostyantyn Anatol'evich LEBEDEV 3
Received: 20/05/2018 • Approved: 08/06/2018
ABSTRACT: The paper is devoted to the development of strategic mechanisms for the future development of the international e-commerce market. It has been proved that by defining the mechanism of protection of information systems of the parties in the global and national e-commerce markets and ensuring its implementation along the entire flow route of virtual resources, it is possible to create objective prerequisites for increasing the potential of the global electronic market, improving the information and communication interaction of industries, regions, corporations within the developing framework of modern network international relations. It is established that the conceptual approaches proposed in the study for the formation and development of the system of international electronic business, as well as the mechanisms for their implementation, will help to increase the efficiency of integration processes with the structures of the global electronic market by optimizing the activity of electronic commerce systems at any level of governance. |
RESUMEN: El estudio está dedicado al desarrollo de mecanismos estratégicos para el desarrollo futuro del mercado internacional del comercio electrónico. Se ha demostrado que al definir el mecanismo de protección de los sistemas de información de las partes en los mercados mundiales y nacionales de comercio electrónico y asegurar su implementación a lo largo de toda la ruta de flujo de recursos virtuales. Es posible crear requisitos previos objetivos para aumentar el potencial del mercado electrónico global mejorando la interacción de información y comunicación de las industrias, regiones y corporaciones dentro del marco en desarrollo de las relaciones internacionales de las redes modernas. Se establece que los enfoques conceptuales propuestos en el estudio para la formación y desarrollo del sistema de negocios electrónicos internacionales, así como los mecanismos para su implementación, ayudarán a aumentar la eficiencia de los procesos de integración con las estructuras del mercado electrónico global. mediante la optimización de la actividad de los sistemas de comercio electrónico en cualquier nivel de gobierno. |
The transition to the information society and the development of e-commerce are governed by consumer interests. The rhythm of this transformation is dictated by the development of information and communication technologies. These kinds of interests are the most important in post-industrial business-driven economic systems that are constantly seeking for more efficient processes, wider markets, and new consumers for their new services.
At the same time, there has been a steady increase in requests from the public, wishing to have higher and higher quality means of communication and access to information for social purposes and self-expression. The spread of e-commerce requires the development of new business models, strategies, and the formation of value-added service providers. However, it is necessary to know how the development of Internet technologies by corporate and individual users affects the situation in the industries and changes the boundaries between electronic and traditional business.
Practice has shown that Internet technologies are dragging all companies into global competition, regardless of their location. This is especially true for companies that produce high-quality goods with low transportation costs. In retail, Internet technologies expand the market beyond the geographic regions in which traditional retailers operate.
In traditional retailing, two consumer electronics stores that are 50 km apart do not compete with each other, and in virtual space their real location may not matter. Thus, e-commerce leads a competitive struggle between sellers from different geographic regions to a qualitatively new level.
The study of the development problems of the international commerce market has found its reflection in papers by Zhukova (2015), Medvedeva and Gladyshev (2013), Pozdnyakova and Shavlovskii (2014), Karpova and Aleshchenko (2016), Usenko (2015), etc. The analysis of scientific sources shows that the problems of assessing the qualitative parameters of the international commerce market remain insufficiently studied, and insufficient attention has been paid to the selection of an optimal strategy in the international commerce market.
The theoretical and methodological basis of the study is the dialectical method of scientific cognition, the provisions in works by domestic and foreign researchers on the methods of international commerce (Kosevich, Matyunina, Zhakevich, Zavalko, and Lebedev 2016; Turkeli 2002). The economic/statistical methods were the instruments to solve these problems.
The application of methods of generalization and systematization, analysis and synthesis made it possible to develop some methodological basics for the preparation of managerial decisions based on the analysis of the international commerce market. In particular, the expertise method was used to develop statistical support for the analysis of functional dependencies, as well as to reasoning of the methodology for studying the interrelationships of qualitative parameters of the international commerce market, their forecasting and modeling.
The information base of the paper is statistical data of state authorities, legislative and normative documents, regulating international commerce, and the results of scientific research carried out by the authors.
In the process of research, it is planned to improve approaches to assessing the qualitative parameters of the international commerce market, to develop measures to coordinate activities between the main market players, to substantiate the strategic mechanisms for the future development of the international commerce market.
The results of the research show that there are no industries that can do without the Internet in their activities. It remains an open question only to what extent the Internet will be used in the traditional business of the company. To successfully integrate the enterprise into the information environment, there must be a number of conditions on which the further development of the electronic commerce system will depend, as well as the quality of the electronic services provided.
Most traditional companies, when trying to implement Internet trading, are meeting serious problems in traditional channels – there are so-called conflicts in distribution channels. The fact is that the transition to electronic sales undermines the business of traditional distributors and dealers. From the transition of the company to electronic sales to end users, its traditional sales channels suffer, losing their market in full or in part.
The transition to e-commerce with the preservation of traditional distribution channels requires a deliberate strategy. The first-priority tasks in the development of a strategic decision to move the company to the level of e-business are: reducing the cost of obtaining the information necessary for business; preparation, operation and support of systems that provide integration into the information infrastructure.
The main task that is solved at the stage of entering the enterprise structure into electronic business is to form the main blocks of the economic project: the investment plan, the list of goods and services provided to the consumer, and the requirements proposed for them, the conceptual architecture of the system, the description of the main processes necessary for the system’s operation, which implements the proposed solutions. At this stage, decisions are made by senior managers of the company and are implemented by authorized subdivisions.
One of the main requirements proposed for the construction of a modern business project in e-commerce is a cost-effective and rapid implementation of the idea into specific solutions that help to improve the process of creating value added chains for a product/service.
Large multinational companies have long and successfully been implementing the Internet as a means of global communication in large-scale projects that require joint efforts of several subdivisions and branches, using the unique information access opportunities provided by the network.
The use of progressive methods of communication within the company leads to an improvement in the manageability of the company by optimizing its organizational structure, the quality of the services provided through faster adaptation to changes in purchasing preferences, as well as accelerating the process of creating a new product and its market testing, expanding the ability to meet the differentiated needs of clients.
The transition to a networked economy is connected with the transition from national to global economic integration. The positive effect of such integration appears precisely from the combination of these two processes: the development of information and communication technologies and the ongoing liberalization of global trade, which is happening today primarily in the service sector.
At the same time, the sphere of information service cannot replace the real sector, but is comprehensively integrated therein, making these spheres more informationally saturated, i.e., e-commerce creates significant opportunities for selling products of the real sector. This universal component leads to the dilution of the earlier existing geographic boundaries of production phases: uneven wealth that used to be between regions and countries will now affect all countries that are part of the global information society.
Deepening the development of the global information economy, expanding the use of Internet systems in the process of creating value added lead to the need for the formation of specialized logistics structures to ensure electronic security of counterparties. This is due to the fact that the use of open communication channels in the electronic logistic system via the Internet, because of the very nature of these systems and the random nature of transactions, creates a potential threat to access to assets of both buyers and sellers. Therefore, the issue of improving the level of security of e-commerce systems is more urgent and important than ever.
The central issue in the security of e-commerce systems is the protection of information. Using the capabilities of a collective information resource should not mean its availability for each user. Appropriate access should be authorized and determined by the rules that are formulated during the creation of the information system.
The analysis and synthesis of fundamental scientific developments in information space protection made it possible to conclude that the most important problems in the security of e-commerce systems include the problem of virus penetration, theft of information, a decrease in the efficiency of computers due to the use of their resources by intruders for their goals, greater speed of modification of threats, imperfection of the legislative base. An important aspect of threats is the threat of information leakage. To date, this often happens due to the storage of data on the mobile devices. Information leakage channels can be presented in Fig. 1.
Figure 1
Information leakage channels in international e-commerce in 2016
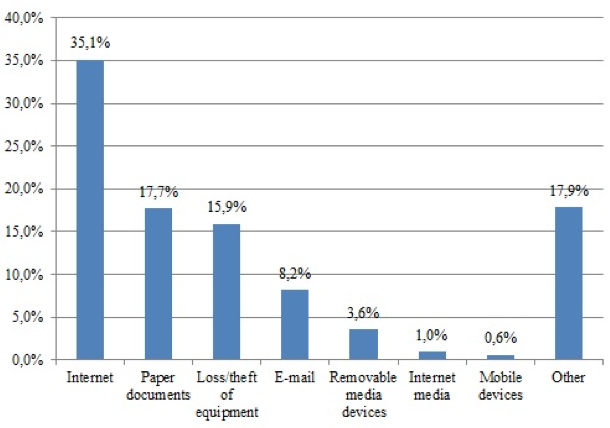
Meantime, first of all, the form of information protection needs to be improved, which is transmitted through browsers and cloud services, e-mail, social networks. The leakage of data via traditional channels is evidenced ever less, as the attackers do not use them, being well aware of the functionality of protective solutions. Most of the sources in 2016 accounted for three main channels: the Internet (35%), paper documents (18%) and equipment loss (16%). At the same time, deliberate leaks most often occur through the Internet, and accidental – in case of loss or theft of equipment.
From the registered 1,396 cases of leakage of confidential information in the world in 2016, which is plus 22% as compared to the leaks registered in 2015, 91.1% represent cases of personal data leakage and payment information (an increase of 7% as compared to 2015).
The second place is taken by trade secrets and know-how (4.2%). The fight against this type of crime in the US and EU countries is carried out by legislative methods, the company that suffered a leak of information being responsible. In the Russian Federation at the moment there is no such mechanism.
As research has shown, the main reasons for violation of information security systems are: irresponsibility, negligence and self-interest of personnel. In 2016, 55% of the perpetrators of information leakage were current or former employees – 54% and 1%, respectively, and through the fault of the malicious agents, 25.8% of the leakage occurred.
A significant share of leakage occurred through contractors, whose personnel had legitimate access to information (4%). More than 1% of the cases recorded the fault of heads of organizations (top management, heads of departments and sectors), users with enhanced access to information (system administrators). So, the main source of infringements of information security is inside most information systems, thus, for each of them, internal protection must be mandatory.
One of the greatest threats for information systems is virus programs that penetrate via different media and global information networks. According to a survey conducted among employees in international e-commerce, threats to Internet security are ranked in the following order (Fig. 2).
At the same time, 87% of respondents expressed support for the need to create an information portal on the security in cyberspace. Undoubtedly, one of the main problems of the development of the global market for international e-commerce is hacker attacks on information systems that cause direct material damage not only to developers of information technologies, but also to their users.
Figure 2
Security threats to international e-commerce via the Internet in 2016
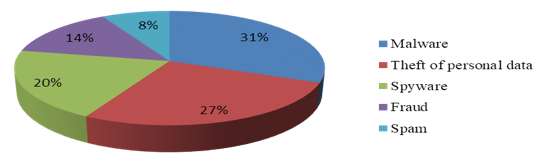
Practice has shown that between hacker groups there is quite a tough competition in the underground market of hacking and trading stolen information. In 2016, every third spyware program was created and every third virus was written in the US, followed by China with 10%, and Germany with 7%.
In addition, the US is also the leader in the number of botnets, which consist of infected computers, through which hackers send out spam and carry out their attacks. In the vast majority of cases, computer owners do not realize that the machine is infected and spends CPU time and traffic for hackers’ purposes.
The number of personal computers drawn into hacker botnets by the end of 2016 amounted to about 1.9 million, with the most spam on the international scale associated with the stock market game and various financial frauds. Among the priority areas of e-commerce, an important role is played by the Internet B2C systems. The main type of those systems – an online shop – is an element of the e-commerce system via the Internet.
At each stage of the purchase through the Internet, different threats can arise. One of them is the substitution of the Web server page of the electronic store. The main way to implement this is to forward user requests to another server. This is especially dangerous when the customer enters his/her bank card number. In addition, it is also possible to enter the database and change order processing procedures, which makes it possible to illegally manipulate the database.
At the stage when an electronic store sends the order confirmation to the customer, there is a possibility of interception of the data transferred in the e-commerce system. All these threats are entirely real, but the emergence of such problems, although it causes considerable inconvenience to the client, is mostly harmful for the store.
The study of existing theoretical postulates and the results of practical activities in the protection of e-commerce systems allowed substantiating a mechanism to manage the system of protection of international e-commerce, based on the integrated use of such elements as legal, organizational and administrative and software and hardware (Fig. 3).
Figure 3
A mechanism to manage the protection system of international e‑commerce
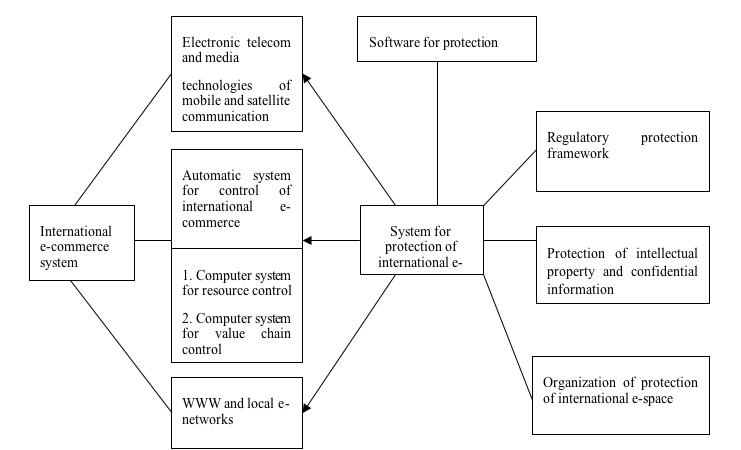
At the same time, the creation of areas for protection of international e-commerce specifies, first of all, the definition of objects and methods of protecting information. The priority objects of information protection include: information resources; separate arrays of documents, arrays of documents in information systems (banks of data of consumers, suppliers, mediators, archives, funds, etc.); information products; the aggregate of the data generated by manufacturers for distribution in material or non-material forms; information services; receipt and presentation of information products to the end-user.
The reliability of the presented strategic mechanisms for the future development of the international e-commerce market is confirmed by the fact that they are based on such types of information services which are provided by consulting firms of electronic commerce and information outsourcing providers: submission of the full text of documents, as well as information on their description and location; issuance of results of analytical processing of information (references, digests, surveys, indexes); obtaining results of factographic information search (tables, dossiers, references); delivery of the results of information research (reports, surveys, classifiers of prospective areas of international commerce).
The most important methods for protecting international e-commerce are: 1) from computer hardware failures: archiving (with and without compression) and file backup; 2) from accidental loss and creation of information that is stored in computer systems: request to confirm the execution of commands that change files; establishment of special attributes of documents and programs; possibility of distinguishing an incorrect action or recovering a mistakenly deleted file; disaggregating users to the resources of the file system; 3) from deliberate distortion of information, vandalism (computer viruses): general methods of software and technical information protection; use of anti-virus programs (Bilman 2013; Huseynova 2015; Bennett and Barkensjo 2005).
Nevertheless, wherever possible, measures should be replaced with more reliable modern physical and technical means. In the process of risk analysis for the system of international e-commerce, it is necessary to study its components, determine the specific locations of the system, assess the feasibility of each specific threat and the expected size of the corresponding losses, choose possible methods of protection and assess their value.
Summing up, it can be noted that by defining the mechanism of protection of information systems of the global and national e-commerce market players and ensuring its implementation along the entire flow of virtual resources, objective prerequisites for increasing the potential of the global electronic market, information and communication interaction of industries, regions, corporations within the framework of the development of modern network international relations will be created.
The proposed conceptual approaches to the formation and development of the system of international e-business, as well as the mechanisms for their implementation, will indeed help to improve the efficiency of integration processes with the structures of the global electronic market by optimizing the activity of e-commerce systems at all levels of governance.
Bennett, R., and Barkensjo, A. (2005). Relationship Quality, Relationship Marketing, and Client Perceptions of the Levels of Service Quality of Charitable Organizations. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 16(1), 81-106.
Bilman, A.S. (2013). Interaction between International Trade and Economic Growth: Evidence from Qualitative Comparative Analysis. International Economics Letters, 2(4), 5-18.
Huseynova, S.M. (2015). The Influence of International Migration on International Trade. European Journal of Economics and Management Sciences, 3, 27-29.
Karpova, V.V., and Aleshchenko, V.V. (Eds.). (2016). Spetsifikatsiya regionalnoi promyshlennoi politiki s ispolzovaniem elementov klasternogo podkhoda (na materialakh Omskoi oblasti) [Specification of Regional Industrial Policy with the Use of Elements of the Cluster Approach (Based on Materials of the Omsk Region)]. Novosibirsk: Institute of Economics and Industrial Engineering, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, (p, 480).
Kosevich, A.V., Matyunina, O.E., Zhakevich, A.G., Zavalko, N.A., and Lebedev, K.A. (2016). Methodology to Estimate the Financial Market Condition. Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 7(7), 1749-1753.
Medvedeva, M.B., and Gladyshev, D.A. (2013). Napravleniya integratsii in-frastruktury rossiiskogo finansovogo rynka s mirovym finan-sovym rynkom: problemy i perspektivy [Directions of Integration of the Infrastructure of the Russian Financial Market with the World Financial Market: Problems and Prospects]. Valyutnoe regulirovanie. Valyutnyi control, 9, 19-32.
Pozdnyakova, A.N., and Shavlovskii, I.P. (2014). Faktory, stimuliruyushchie mezhdunarodnuyu logistiku i mezhdunarodnuyu torgovlyu [Factors That Stimulate International Logistics and International Trade]. Mir sovremennoi nauki, 6(28), 82-84.
Turkeli, S. (2002). International Relation, Organization, and Policy: International Trade. Sage Public Administration Abstracts, 28(4), 521-523.
Usenko, O.I. (2015). Model vnutrennego finansovogo kontrolya v byudzhetnom sektore kak bazis sistemy gosudarstvennogo finansovogo kontrolya subekta Rossiiskoi Federatsii [The Model of Internal Financial Control in the Budget Sector as a Basis of the System of State Financial Control of the Region of the Russian Federation]. Vestnik Rossiiskogo ekonomicheskogo universiteta im. G.V. Plekhanova, 6(84), 94-106.
Zhukov, V.N. (2015). Informatsionnye strategii vo vnutrennem finansovom kontrole korporatsii [Information Strategies in the Internal Financial Control of Corporations]. Bukhgalterskii uchet, 9, 89-92.
1. Federal State Autonomous Institution of Higher Education "Moscow State Institute of International Relations (University) of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation", 119454, Russia, Moscow, Vernadskogo Ave., 76
2. Federal State Autonomous Institution of Higher Education "Moscow State Institute of International Relations (University) of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation", 119454, Russia, Moscow, Vernadskogo Ave., 76
3. Institute for Tourism and Hospitality, 125438, Russia, Moscow, Kronshtadtskiy Blvd., 32a, E-mail: qwer20003@rambler.ru